In today's hyper-competitive marketplace, brands that thrive are those that place customer needs and experiences at the core of their marketing strategy. Customer-centric marketing isn't just a buzzword—it's a fundamental approach that drives engagement, loyalty, and sustainable growth by focusing on delivering genuine value to your audience.
What is Customer-Centric Marketing?
Customer-centric marketing is an approach that prioritizes the needs, preferences, and pain points of your customers throughout all marketing activities. Rather than focusing solely on promoting products or services, it emphasizes creating meaningful connections and delivering relevant experiences that address specific customer challenges.
The best marketing doesn't feel like marketing—it feels like a solution to a problem the customer didn't even know they could solve.
Key Principles of Customer-Centric Marketing
Building a truly customer-centric marketing strategy requires embracing several core principles that should guide all of your marketing decisions and activities:
1. Deep Customer Understanding
The foundation of customer-centricity is comprehensive knowledge of your audience. This goes beyond basic demographics to include psychographics, behavioral patterns, motivations, and pain points. Invest in both quantitative research (surveys, analytics) and qualitative insights (interviews, focus groups) to develop detailed customer personas that represent your key audience segments.
Pro tip: Schedule regular customer interviews—aim for at least 5-10 per quarter—to maintain an updated understanding of evolving needs and expectations. These conversations often reveal insights that quantitative data alone would miss.
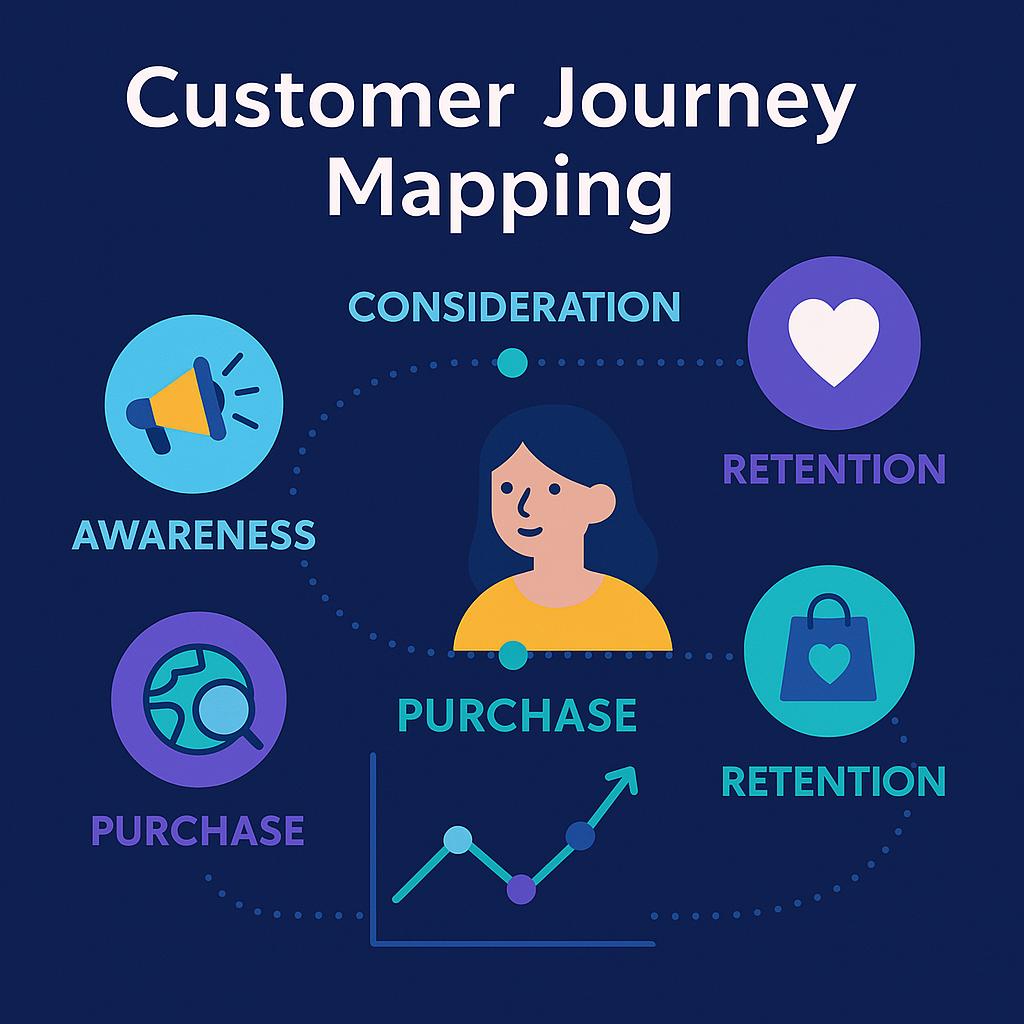
2. Journey-Based Marketing
Map your customer's journey from initial awareness through consideration, purchase, and post-purchase experiences. Identify the key touchpoints where your brand interacts with customers and optimize each one to address specific needs at that stage. This approach ensures you're delivering the right message through the right channel at the right time.
For example, a B2B software company might create educational blog content for the awareness stage, detailed comparison guides for the consideration stage, and onboarding tutorials for the post-purchase stage—each addressing the specific questions customers have at that point in their journey.
3. Value-Driven Content Strategy
Shift your content focus from product features to customer outcomes. Create resources that help solve problems, answer questions, or achieve goals that matter to your audience. This builds trust and positions your brand as a valuable resource, not just another company pushing products.
// Example content mapping framework
const contentMapping = {
awarenessStage: {
customerQuestions: ['How do I solve X problem?', 'What are the best practices for Y?'],
contentFormats: ['Blog posts', 'Social media content', 'Educational videos'],
valueMetrics: ['Engagement rate', 'Time on page', 'Social shares']
},
considerationStage: {
customerQuestions: ['How does your solution compare to alternatives?', 'What results can I expect?'],
contentFormats: ['Case studies', 'Comparison guides', 'Webinars'],
valueMetrics: ['Lead conversion rate', 'Webinar attendance', 'Resource downloads']
},
decisionStage: {
customerQuestions: ['How do I implement this?', 'What's the ROI?', 'Who else has succeeded with this?'],
contentFormats: ['ROI calculators', 'Implementation guides', 'Customer testimonials'],
valueMetrics: ['Sales conversion rate', 'Sales cycle length', 'Deal size']
}
};4. Personalization at Scale
Today's customers expect personalized experiences. Leverage data and marketing technology to deliver tailored content, recommendations, and offers based on individual preferences, behaviors, and needs. Start with segmentation based on key attributes, then progress to more sophisticated personalization as your capabilities mature.
A retail brand might begin with simple personalization (email segmentation by purchase history) before advancing to dynamic website content that changes based on browsing behavior, AI-powered product recommendations, and omnichannel experiences that maintain context across touchpoints.
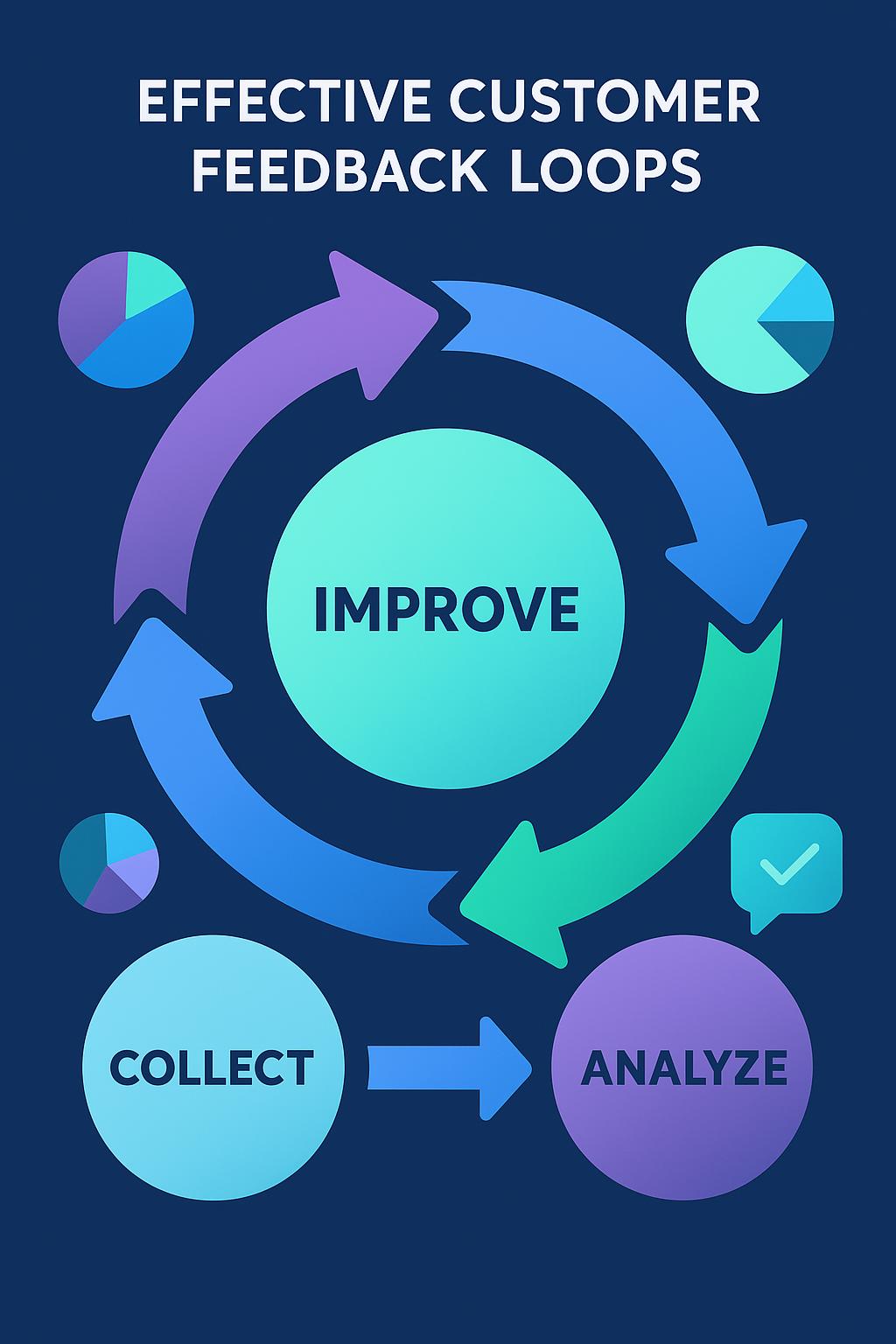
5. Customer Feedback Loops
Establish systems for continuously collecting, analyzing, and acting on customer feedback. This includes formal mechanisms like surveys and reviews, as well as monitoring social media, support interactions, and other channels where customers share their experiences.
The most customer-centric organizations don't just gather feedback—they close the loop by communicating back to customers how their input has shaped products, services, and experiences. This demonstrates that you're truly listening and values their perspective.
Implementing a Customer-Centric Marketing Strategy
Moving from theory to practice requires a structured approach. Here's a practical implementation framework to transform your marketing into a truly customer-centric operation:
Step 1: Audit Your Current State
Begin by assessing your existing marketing approach through a customer-centric lens. Evaluate all touchpoints, messages, and experiences from the customer's perspective. Identify gaps between customer expectations and your current delivery, as well as opportunities to create more customer-focused experiences.
Use methods like mystery shopping, customer journey audits, and content inventories to get an objective view of your current state. Document specific pain points and friction areas that need improvement.
Step 2: Develop Comprehensive Customer Personas
Create or refine your customer personas based on both quantitative and qualitative research. Each persona should include demographic information, goals, challenges, information preferences, and decision-making factors. These personas will guide your content creation, channel strategy, and messaging.
For B2B companies, ensure your personas include information about the buying committee and different stakeholder perspectives. For B2C brands, consider lifestyle factors and emotional drivers that influence purchase decisions.
Step 3: Map the Customer Journey
Develop detailed journey maps for each persona, documenting their path from initial problem awareness through research, evaluation, purchase, and ongoing engagement. Identify key touchpoints, information needs, emotional states, and potential barriers at each stage.
The most effective journey maps go beyond simple flowcharts to include the customer's goals, questions, emotions, and actions at each stage, along with the specific touchpoints and content that will best serve their needs.
Step 4: Align Content and Channels to the Journey
Based on your journey maps, develop a content strategy that delivers relevant, valuable information at each stage. Map specific content formats, topics, and distribution channels to the identified customer needs and preferred touchpoints.
Create a content calendar that balances content for different journey stages and personas. Prioritize high-impact pieces that address critical customer questions or pain points at decisive moments in their journey.
Step 5: Implement Personalization
Start with basic segmentation and gradually build more sophisticated personalization capabilities. Begin by personalizing email communications based on customer attributes and behaviors, then expand to website content, product recommendations, and cross-channel experiences.
Remember that effective personalization balances relevance with respect for privacy. Be transparent about data collection and use, and always provide value in exchange for the information customers share with you.
Step 6: Establish Measurement Framework
Develop metrics that measure both business outcomes and customer experience quality. Balance traditional marketing KPIs (conversion rates, revenue) with customer-centric metrics like satisfaction scores, effort scores, and loyalty indicators.
Create dashboards that make these metrics visible to all stakeholders and review them regularly to identify areas for improvement. Celebrate wins and address challenges proactively.
What gets measured gets managed. When you measure customer value alongside business value, you naturally orient your marketing toward customer-centricity.
Step 7: Foster Cross-Functional Collaboration
True customer-centricity requires alignment across departments. Marketing must collaborate closely with sales, product, customer service, and other teams to ensure consistent experiences. Create shared goals, regular cross-functional meetings, and integrated workflows to break down silos.
Consider establishing a customer experience council with representatives from different departments to coordinate initiatives and ensure alignment around customer needs.
Real-World Success Stories
Let's examine how three diverse companies have successfully implemented customer-centric marketing approaches:
Case Study 1: B2B Software Company
A mid-sized B2B software provider reorganized their marketing around specific customer jobs-to-be-done rather than product features. They created specialized content hubs addressing the core challenges of different buyer personas and implemented an account-based marketing approach for key prospects.
Results: 67% increase in marketing qualified leads, 24% reduction in sales cycle length, and 35% improvement in customer retention within 12 months.
Case Study 2: Consumer Financial Services
A financial services company shifted from product-centric marketing to life-stage marketing, creating personalized journeys based on major life events (marriage, home buying, retirement planning). They developed educational resources, interactive tools, and community forums to support customers through these transitions.
Results: 43% increase in customer engagement, 29% higher cross-selling success, and 18% improvement in Net Promoter Score.
Case Study 3: E-commerce Retailer
An online retailer implemented a sophisticated personalization engine that tailored the shopping experience based on browsing history, purchase behavior, and stated preferences. They also revamped their content strategy to focus on lifestyle content that addressed customer interests beyond products alone.
Results: 52% increase in average order value, 38% improvement in repeat purchase rate, and 47% higher email engagement.
Common Challenges and Solutions
While the benefits of customer-centric marketing are clear, implementation isn't without challenges. Here are some common obstacles and practical solutions:
Challenge 1: Siloed Data
Many organizations struggle with fragmented customer data across multiple systems, making it difficult to develop a unified view of the customer.
Solution: Invest in a customer data platform (CDP) that aggregates information from various sources. Begin with the most critical data points and expand over time. Focus on actionable insights rather than perfect data integration.
Challenge 2: Short-Term Revenue Pressure
The pressure to deliver immediate results can conflict with customer-centric approaches that may take time to yield financial returns.
Solution: Develop a balanced scorecard that includes both short-term performance metrics and customer-centric indicators. Communicate the long-term value of customer-centricity to stakeholders and find quick wins that demonstrate initial success.
Challenge 3: Organizational Resistance
Shifting to a customer-centric approach often requires changes in processes, metrics, and even company culture, which can face resistance.
Solution: Start with pilot projects that demonstrate value, then expand gradually. Share customer feedback and success stories to build momentum. Involve team members in the process to foster ownership and reduce resistance.
Conclusion: The Future of Customer-Centric Marketing
As markets become increasingly competitive and customers more discerning, customer-centricity will transition from competitive advantage to basic requirement. The most successful marketers will continuously deepen their understanding of customers and innovate to meet evolving needs.
Remember that becoming truly customer-centric is a journey, not a destination. It requires ongoing commitment, continuous learning, and constant adaptation. Start where you are, with the resources you have, and progressively build more sophisticated capabilities that place customers at the center of everything you do.
The rewards—increased loyalty, higher lifetime value, more efficient acquisition, and sustainable growth—make this one of the most valuable transformations your marketing organization can undertake.



